Dr. Tobias Pöhlmann
Ronneburger Straße 74
07546 Gera
Phone (): +49 365 77347180
info@xnapharma.com
https://xnapharma.com
During the last years, XNApharma performed intensive basic research in order to identify protease candidates that are specifically expressed in cancer cells and show a selective protease activity, identified protease substrates, develloped coupling chemistries, and investigated the mode of action.
siRNA-inhibition by peptide coupling
The Peptide-siRNA-Prodrug technology platform aimes to induce RNA interference selectively in specific cells. The bound peptide is intended to inhibit the siRNA activity. After peptide cleavage in target cells, the siRNA induces RNAi activity. Therefore, intensive basic research studies have been performed in order to identify possible locations on the siRNA that inhibit the molecule after peptide coupling.
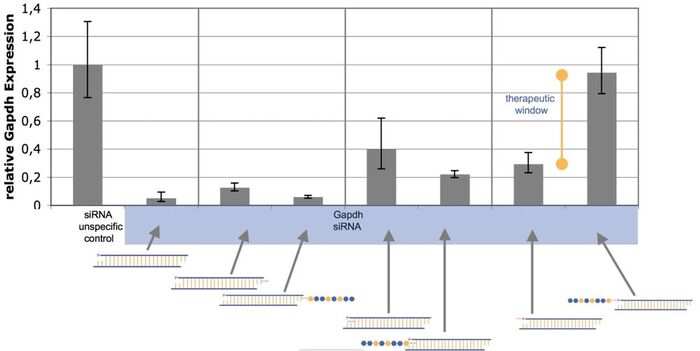
The figure above displays the activity of conventional GAPDH siRNA. Additionally, activity of siRNAs after peptide and linker modifications at the 3' and 5' ends of the antisense strand as well as the 5' base are shown. In result, only the 5' antisense strand is sensitive enough to completely inhibit the siRNA displaying the therapeutic window of the prodrug.
Peptide-siRNA prodrug activation
Protease cleavage is a sensitive process. Efficient cleavage requires, e.g. optimal pH environment, access to the target substrate or specific salt concentration. Selection of target proteases and their substrates is a complex process and requires multiple optimisation steps. At the same time, the intracellular plasma provides a specific and stable environment for the Peptide-siRNA-Prodrug platform.
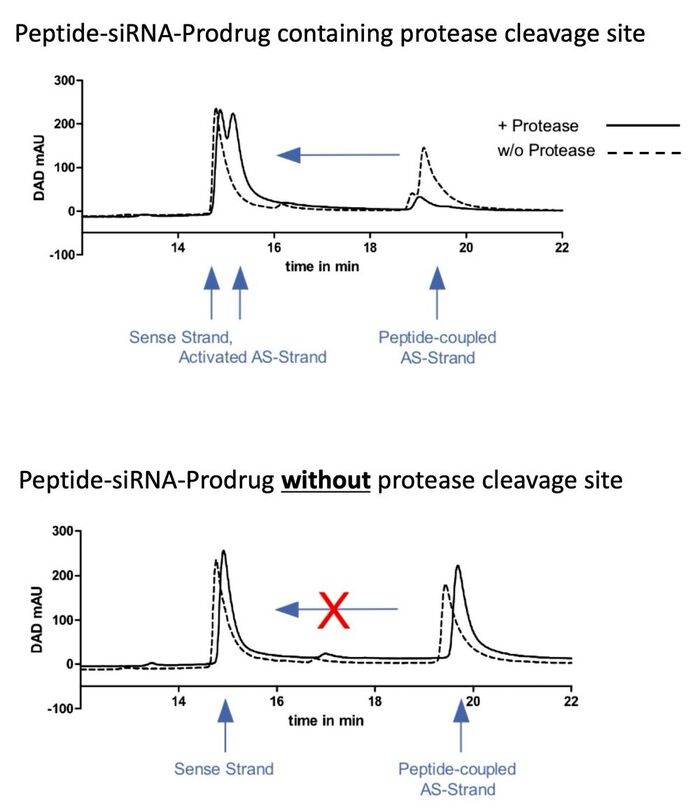
The data on the right shows an example of Peptide-siRNA activation in vitro by a specific protease. This is indicated by a HPLC-shift of the antisense-strand after addition of the respective protease, whereas the same protease was not able to cleave a coupled nonsense-peptide as indicated by stable UV-spectra.
This data proves firstly the ability of the protease to cleave a specific substrate from the siRNA antisense strand and secondly the specificity of the used protease to its target peptide.
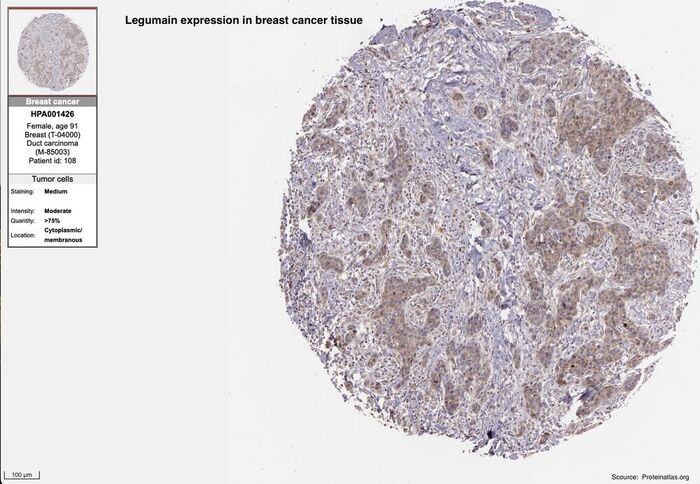
Protease expression in primary cancer tissue
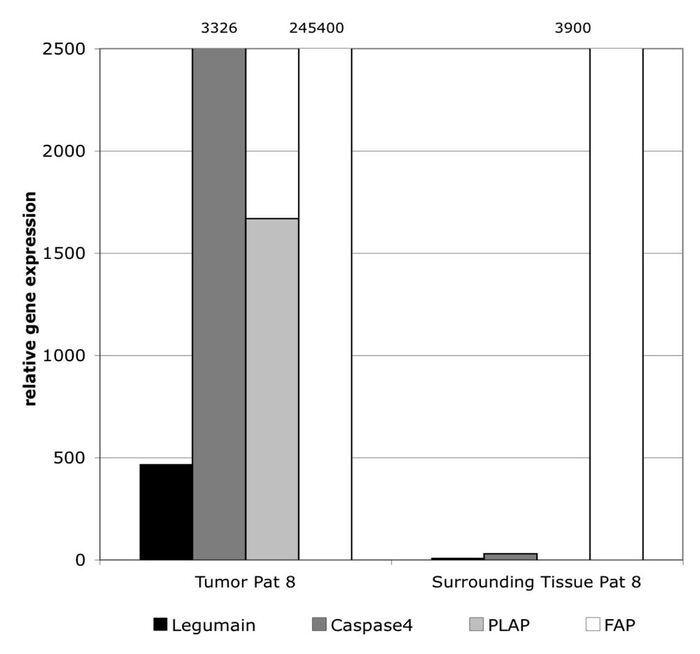
Cancer tissues in general show specific gene expression pattern. The expression of several proteaseses is also midifed during cancer development. Especially cytoplasmatic proteases are of interest to be used as activating machenisms for the Peptide-siRNA-Prodrug platform.
The figure below is displaying a microscopy image of a patient breast cancer sample showing an elevated protein expression of legumain. Legumain is one of the proteases which can selectively activate XNApharma drug candidates.
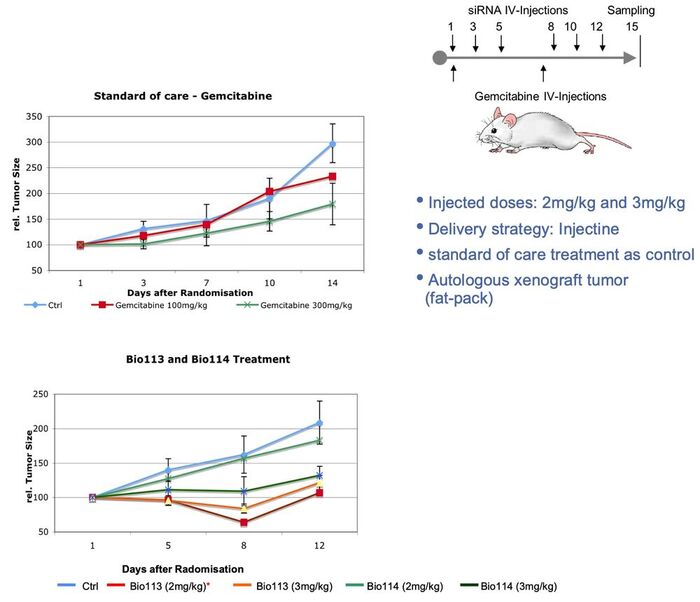
Peptide-siRNA-Prodrug in vivo efficacy
As proof of concept, several studies to reduce tumor growth in breast cancer xenotranplant mouse models have been performed. As stadard of care, high dose Gemcitabine treatment was applied in order to show the impact of Peptide-siRNA-Prodrug treatment.
XNApharma's drug candidates were repeatedly injected intraveniously followed by tumor size analysis, histology and gene expression analysis. As an example of an animal study, the figure below shows the inhibition of tumor growth during treatment by standard of care (Gemcitabine) and Peptide-siRNA-Prodrug candidates. In result, drug candidates showed improved efficacy compared to standard therapy.
During these animal studies, Peptide-siRNA-Prodrugs showed excellent safety and tolerability eventhough bioavalability was limited by the particular delivery strategy.
© XNApharma GmbH, Ronneburger Straße 74, 07546 Gera
Source: https://xnapharma.com/Preclinical_development

 Copyright© XNApharma GmbH
Copyright© XNApharma GmbH